Together with VTT, LUT University is studying how carbon dioxide emissions from forest industry can be utilised in producing plastics, for example. Carbon dioxide can also be used to produce aviation fuel – and even food.
The right amount of carbon dioxide helps the earth remain habitable. In addition, it can be used in various industrial manufacturing processes opening up new opportunities for eliminating carbon dioxide emissions before they are released into the atmosphere.
“Even though carbon dioxide can be beneficial, its production should not be considered valuable in itself. The focus should be on developing processes in which no excess carbon dioxide will be generated in the first place,” says Kristian Melin, professor of process and factory design of biorefining at LUT University.
Carbon dioxide can be used to make many products currently produced using oil. One of them is plastic. Melin says that they currently study the production of plastics based on carbon dioxide and hydrogen in the joint Forest CUMP project of LUT and VTT – CUMP means Carbon dioxide Utilization for Materials and Plastics.
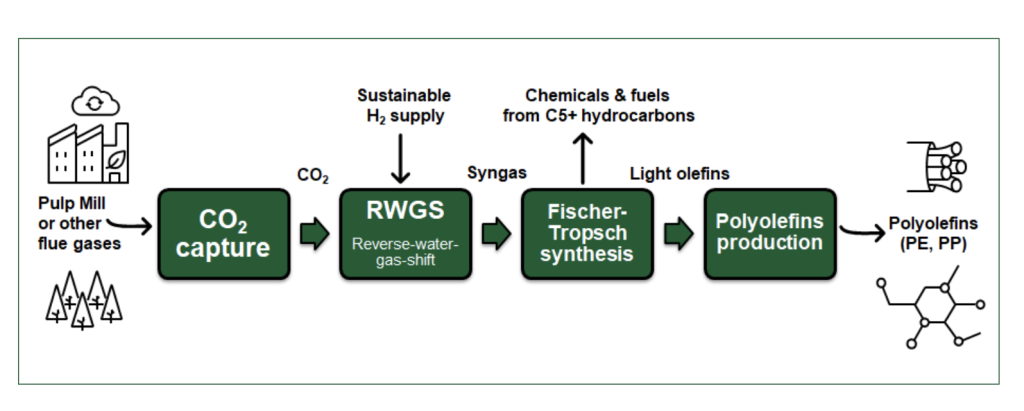
In the project, the most common types of plastic, polythene and polypropylene, will be produced from carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The carbon dioxide used for production is taken from the forest industry, whose bio-based carbon dioxide emissions correspond to almost half of Finland’s current emissions. LUT’s role in the project is to study the cleaning and utilisation of carbon dioxide emissions of the forest industry.
“Plastic produced from carbon dioxide is an opportunity for the future. Currently, it can be done technically, but it is still quite expensive. At least 95% of the world’s plastic is still produced from oil. However, plastic is also produced sustainably, for example from biomass, which is already common” Melin says.
The CIMANET doctoral training pilot funded by the Ministry of Education and Culture has just started a project in which biodegradable plastic is made from pulp, carbon dioxide and hydrogen to replace old oil-based plastics in packaging, for example. In addition to LUT, eight other Finnish universities are involved in CIMANET.




